Ⅰ. 서 론
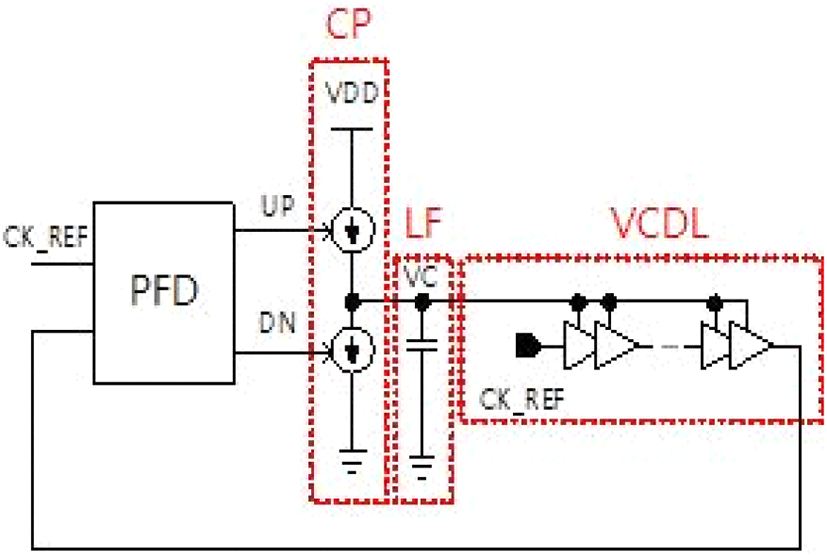
Delay locked loop(DLL)은 high speed microprocessor에서 clock을 생성하거나, digital converter나 mixed signal을 설계할 때, Time calibration을 위한 multiphase clock을 생성하기 위해 사용된다. DLL의 작동 원리는 loop가 닫혀있는 상태에서 negative feedback loop를 통해 random error가 주기마다 누적되지 않기 때문에 PLL보다 적은 jitter를 가진다. 또한 PLL에 비해 구조가 단순하고, 동작 특성상 안정적이며, 소음에 영향을 적게 받는다. DLL은 크게 Analog DLL과 All digital DLL(ADDLL)로 구분된다. 그림 1은 analog DLL의 block diagram이다. Phase detector (PD), charge pump(CP), loop filter(LF)와 voltage controlled delay line(VCDL)으로 구성되어 있으며, analog controlled delay line은 jitter성능이 우수하다. 하지만 lock까지 시간이 많이 걸리고, 소비전력이 크고 LF에 의해 layout size가 크며, 최신 회로에 적용하기가 힘들다. 이러한 단점을 극복하기 위해 Digital DLL[1]이 제안되었다. 높은 Operating frequency와 낮은 전력 소비량은 Digital DLL의 필요성을 느끼게 한다. 최근 Mixed mode ACC-DAC based design[2]에서는 fast lock, low power와 우수한 jitter 성능에 대한 사례가 보고되고 있으며, Accumulator(ACC)의 비활성화로 인해 DAC에서는 lock되어 있는 동안 고정된 값을 출력한다. 그래서 온도나 supply voltage의 변화에 대한 phase error를 detecting이 어렵다. 이러한 단점을 극복하기 위해 Semi digital DLL[1]이 제안되었다. ACC 비활성화로 인해 DAC는 lock 중에 고정값을 가지고 있어 원치 않는 processor나 온도, supply voltage 차이로 인해 lock 이후 phase error를 detecting하기 힘들다.
Ⅱ. 본 론
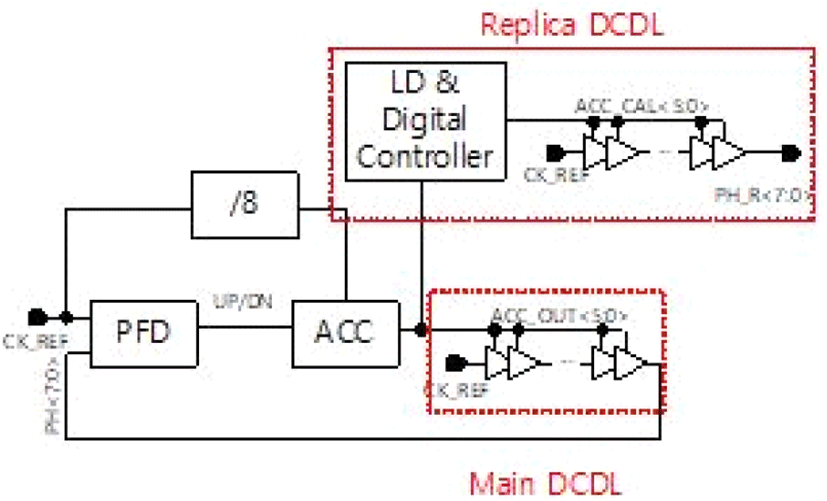
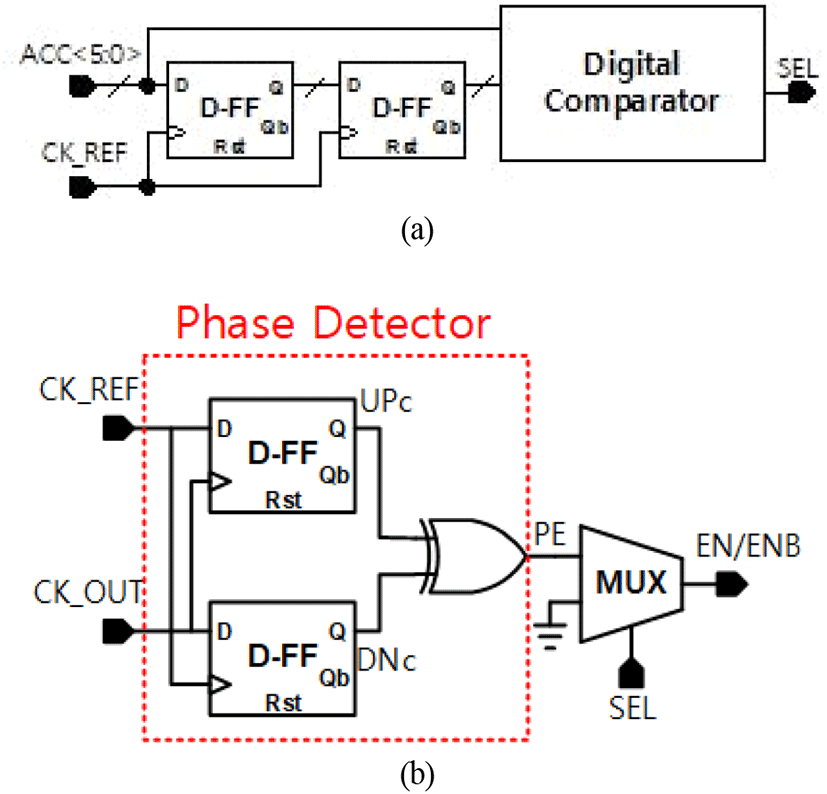
기존의 Semi digital DLL의 경우, VCDL 내부의 delay를 analog signal을 통해 조정할 뿐만 아니라, PVT 변화로 인해 lock 이후 phase error를 검출할 수 없다[1]. 이를 개선하기 위한 DLL구조를 그림 2에 나타내었다. PFD 출력의 UP/DN 신호는 lead하거나 delay 되는 phase 차이를 결정한다. UP/DN 신호에 따라 ACC는 감소하거나 증가하는 시간을 count하게 되고, DCDL 내부의 delay를 조정하게 된다. DLL이 lock이 되면 ACC는 lock detect 회로에 의해 비활성화되고, 고정된 digital code를 출력하게 된다. 즉, DCDL 내부의 delay는 고정되게 된다. lock 이후 PVT 보상을 위한 회로는 원치 않는 processor나 온도, supply voltage 의 변화로 인한 phase error를 지속적으로 check해야 한다. PVT 보상을 위한 회로가 phase error를 검출하고, ACC가 delay를 다시 설정하고 phase error를 취소하여 loop를 다시 lock시킨다. ACC는 높은 주파수에서 전력소모가 심한 Block이다. 전력 소모 감소와 DCDL의 총 delay가 최대일 때, 1주기안에 모든 단계를 커버하기 위해 reference clock을 8분주한 뒤 ACC에 적용하여 낮은 주파수를 가져가 ACC의 전력 소모를 줄이게 한다. 그림 3은 제안된 DLL의 타이밍도이다.
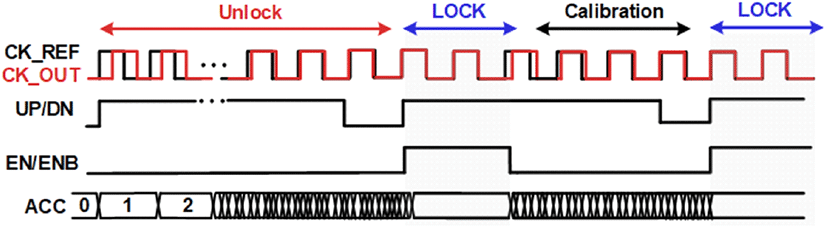
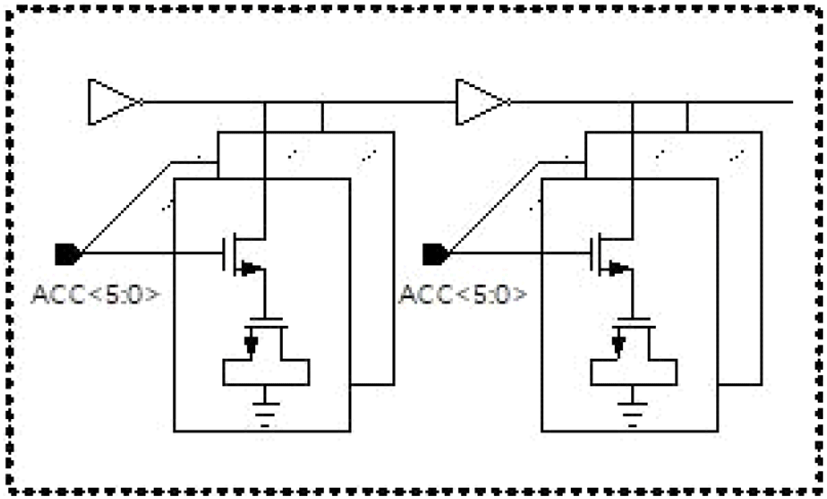
그림 4는 제안된 Digitally controlled delay cell이다. 여기서 2개의 인버터는 Binary weighted switches와 MOS capacitor로 계단 형식으로 구현된다. ACC의 binary 출력은 각 인버터의 출력에서 등가 capacitance를 증가시키거나 감소시켜 delay를 조정한다. Mismatch를 줄이기 위해 binary weighted transistor는 layout을 진행할 때 중심점을 기준으로 병렬로 구현한다.
Lock 상태에서는 CK_REF와 CK_OUT의 위상 차이가 1LSB로 제한되고, ACC는 Periodical pattern(n, n+1, n, n+1, …)을 갖는다. 그림 5(a)와 같이 하나의 LSB error를 제거하기 위해 ACC의 출력은 두 번 이동한 다음 비교된다. ACC 값과 shift된 값이 같은 경우, SEL과 PE신호는 각각 ‘1’과 ‘0’ 이된다. 따라서 CK_ACC는 참고문헌 [3]에서 제안된 것과 같이 비활성화된다. 그림 5(b)에서 제안된 PVT 보상 회로는 간단한 PD와 MUX로 구현된다. 이 block에 의해 lock이 되기 전 phase error detecting을 비활성화 되도록 SEL 신로를 ‘0’으로 설정하고, 주 PFD는 phase error를 detecting한다. Lock 이후 phase error가 발생하면 PE신호가 ‘1’이 된다. Simple phase detector는 ACC를 활성화 시킨다. 앞에서 말한 바와 같이 Current consumption과 stability 문제를 줄이기 위해 CK_REF를 8분주한 뒤 ACC에 적용한다.
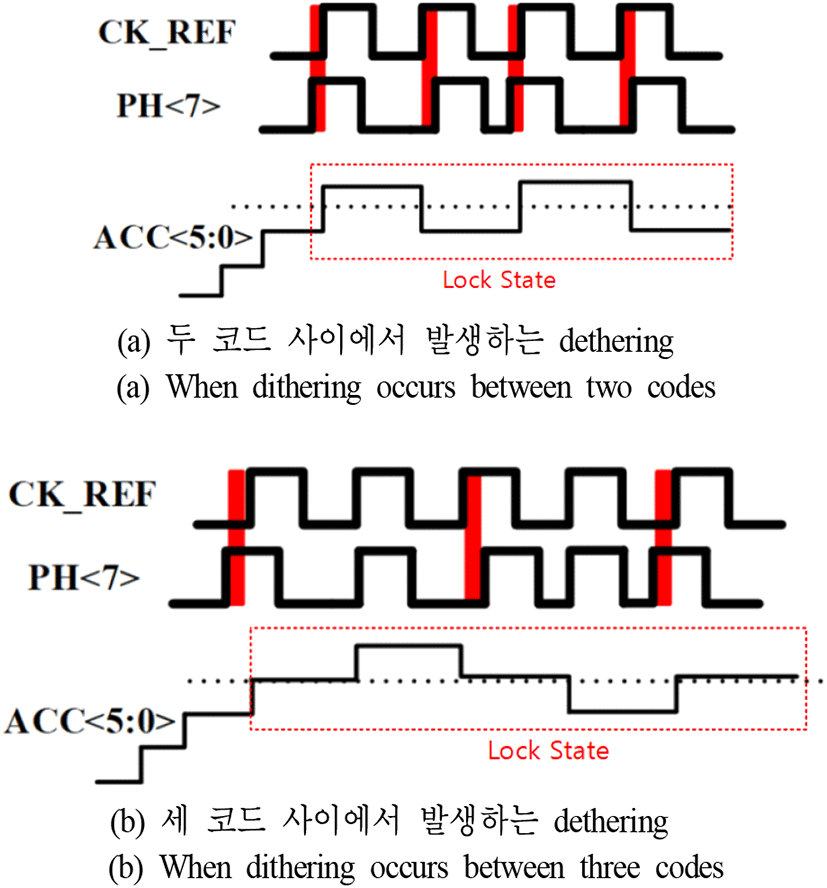
또한 Lock 이후 phase detector로 들어오는 두 신호 CK_ REF와 DCDL의 출력이 동일하게 들어오게 되면 lock state를 중심으로 dithering 현상이 발생한다. 이 현상이 발생하면 ACC 출력이 두 코드(±1 LSB) 사이를 왔다 갔다 하며, 그림 6(a)와 같이 ADDLL의 jitter를 증가시킨다. 또 PD의 Zero dead zone으로 인해 또 다른 error가 발생한다. Dithering 현상을 제거하고, jitter를 줄이기 위해서는 ACC의 출력값을 고정하고, DCDL 내부의 delay가 조정되지 않도록 유지해야 한다. Loop detecting에서 그림 6(a)의 경우, ACC 출력 패턴이 두 코드(n, n+1, n, n+1, n, …)사이에서 검출될 때의 timing diagram이고, 그림 6(b)의 경우, ACC 출력 패턴이 세 코드(n-1, n, n+1, n, n-1, n, n+1, …)사이에서 검출될 때의 timing diagram이다.
Ⅲ. 시뮬레이션 결과 및 분석
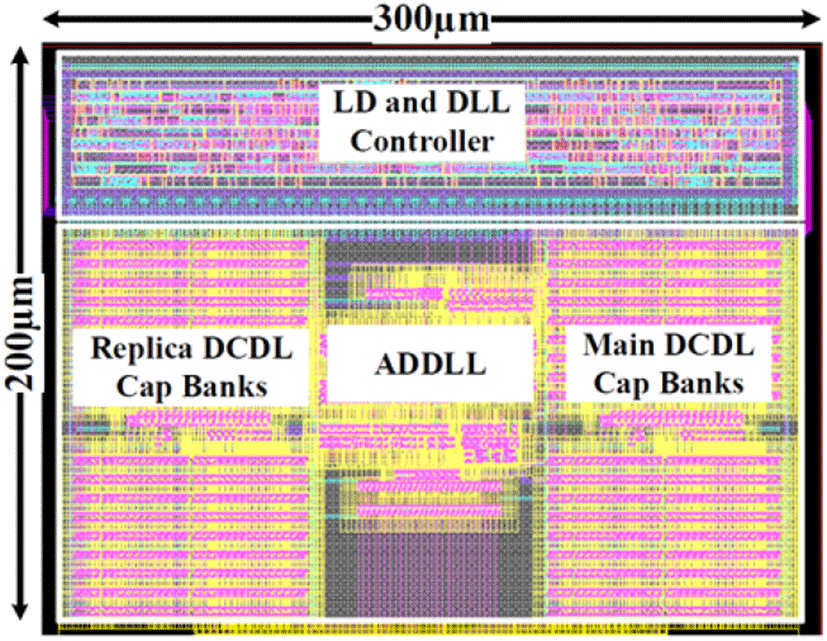
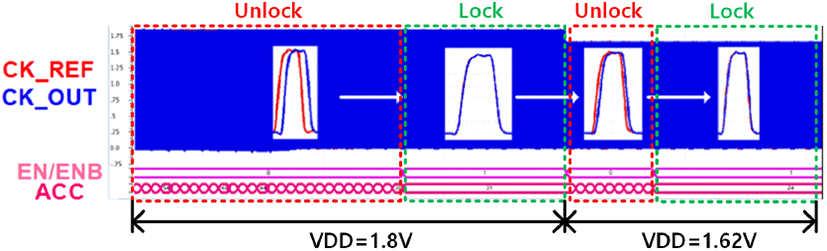
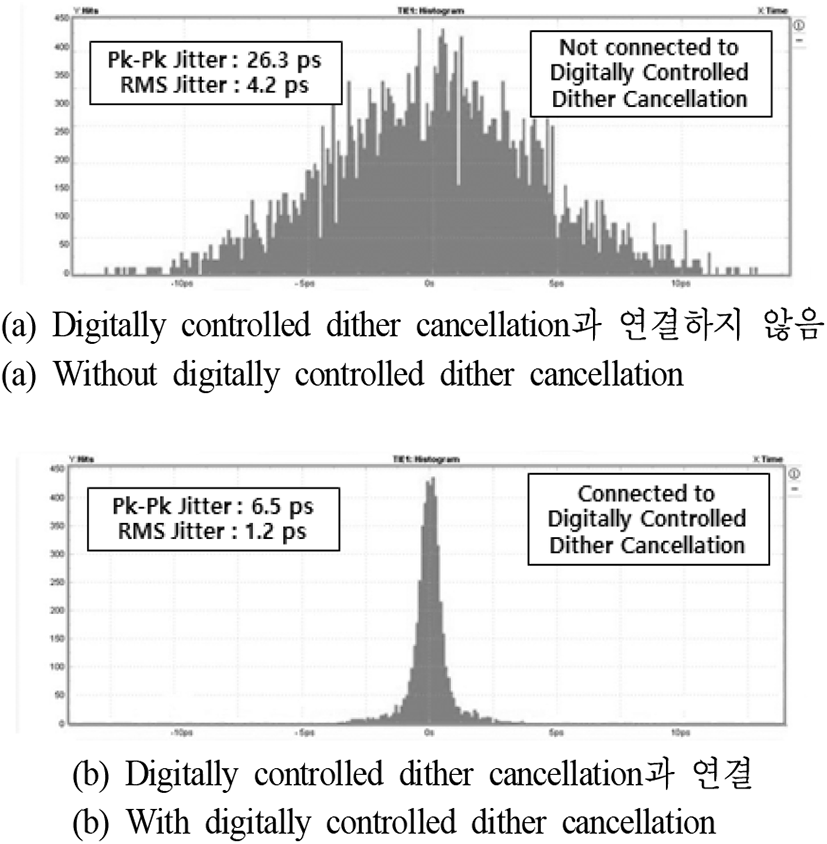
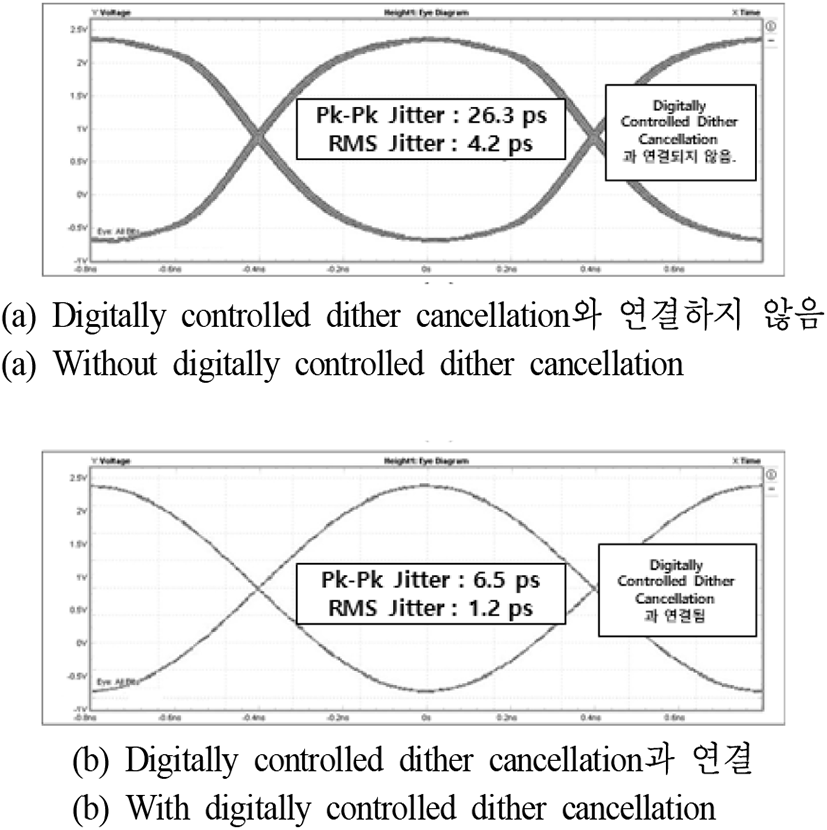
제안하는 ADDLL 회로는 그림 7과 같이 180 nm 표준 CMOS 공정에서 250×300 μm의 사이즈로 설계되었다. 625 MHz의 operating frequency와 1.8 V의 supply voltage에 전류를 6.5 mA를 소비한다. 시뮬레이션 결과는 그림 8에 나타나 있다. ACC 패턴에 따라 ADDLL 회로가 lock이 되는지 확인한다. Lock 이후 PVT 변동을 모델링하기 위해 VDD를 10 % 감소시켜 1.8~1.62 V까지 변화를 주어 확인한다. VDD variation 이후 PD에 의해 phase error가 감지되고, ACC가 패턴을 따르지 않는다. 따라서 ADDLL의 close loop와 ACC 값 update에 의해 생성된 phase error가 사라진다. 측정 결과, digitally controlled dither cancellation과 결합하기 전 peak to peak jitter는 26.3 ps이고, RMS jitter는 4.2 ps이다. Digitally controlled dither cancellation 결합 후 peak to peak jitter는 6.5 ps이고, RMS jitter는 1.2 ps이다. 그림 9(a)는 digitally controlled dither cancellation과 연결하지 않은 상태로 ADDLL의 jitter특성을 측정한 것이고, 그림 9(b)는 digitally controlled dither cancellation과 연결하고 측정한 데이터이다. 그림 10(a)는 Digitally controlled dither cancellation과 연결한 상태로 측정한 eye diagram이고, 그림 10(b)는 digitally controlled dither cancellation과 연결하고, 측정한 eye diagram이다. 표 1은 다른 최근 논문과 요약 비교한 표이다.
| Parameter | Recent designs | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| This work | Ref [2] | Ref [4] | |
| Process | 180 nm | 180 nm | 130 nm |
| Power supply | 1.8 V | 1.8 V | 1.5 V |
| Area (mm2) | 0.075 | NA | 0.08 |
| Power consumption (mW) | 12 @ 625 MHz | 7.85 @ 625 MHz | 26 @ 180 MHz |
| Operating frequency (MHz) | 350-900 | 20-625 | 80-450 |